Have you ever found yourself needing to reach a computer that's, you know, just not physically in front of you? Perhaps it's a machine in another room, or maybe even an industrial PC at a far-off site, or a tiny device doing important work somewhere else. That feeling of needing to get something done, but being stuck because you're not there, it's pretty common, actually. Luckily, there's a whole world of tools that let you take control from a distance, and VNC is a big part of that.
We're going to look closely at how VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, helps folks manage things from afar, especially when it comes to what we call the Internet of Things, or IoT. Think about those smart gadgets or specialized systems that need a bit of tending to without someone having to physically go and plug in a keyboard and mouse. It's a really useful way to stay connected, and we'll be focusing on how you can get started with some free options, which is, you know, a pretty sweet deal for most people.
So, if you're curious about how to gain that kind of remote access, or if you're already familiar with the idea but want to find some great free VNC remote IoT download choices, you've definitely come to the right spot. We'll walk through some popular programs, talk about how to get them running, and even touch on some of the little bumps you might hit along the way, using some real-world experiences to help you out, too. It's all about making your life a bit easier when it comes to managing distant machines, after all.
- Barbara Spear Webster Bio
- Scout Masterson Car Accident
- Where Is The West Highway In Sneaky Sasquatch
- Sone 786 Video
- Suzanne Ad Wilkinson
Table of Contents
- What is VNC and Why Does It Matter for Remote IoT?
- Exploring Free VNC Options: Your Download Guide
- VNC Clients for On-the-Go Control
- Security and Best Practices for Your VNC Setup
- Setting Up a VNC Server: A Quick Guide
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is VNC and Why Does It Matter for Remote IoT?
So, you might be asking, "What exactly is VNC?" Well, in a nutshell, it's a system that lets you see and interact with a computer's desktop from somewhere else. It's like having the computer's screen, keyboard, and mouse right in front of you, even if that computer is, you know, miles away. This works by having a "server" program running on the distant computer and a "viewer" or "client" program on your local machine. The server sends screen updates, and your client sends back your mouse and keyboard actions. It's pretty clever, actually.
The Basics of Remote Access
Remote access, in general, is about connecting to a computer or network from a different location. People use it for all sorts of things, like helping a family member with their computer problems, working from home, or managing servers in a data center. VNC is just one of the ways to do this, but it's a very popular one, especially because there are so many free options available, which is, you know, a big plus for a lot of users. It really opens up possibilities for managing things without needing to be physically present, and that's a huge convenience, in some respects.
VNC in the IoT Space
Now, when we talk about VNC and the Internet of Things (IoT), things get even more interesting. IoT often involves small, specialized devices that might not have their own screen or a convenient way to plug in a keyboard. Think about a smart thermostat, a sensor array in a factory, or even an industrial PC on a production line. Sometimes, you need to access the graphical interface of these devices to configure them, check their status, or troubleshoot something. VNC can be a perfect fit here, allowing you to visually interact with these devices as if you were sitting right in front of them, which is, like, super helpful for maintenance and monitoring.
- Gloria Loring
- Queenpussybossv Onlyfans Leaked
- Greg Daniels Net Worth
- Oliver Stone Net Worth
- Is Jack Pratt Disabled
Exploring Free VNC Options: Your Download Guide
There are quite a few VNC programs out there, but we're focusing on the ones that won't cost you anything to get started. These free options are incredibly capable and can handle most remote access needs, especially for personal use or small-scale IoT projects. It's really about finding the one that fits your particular situation best, you know, because they each have their own little quirks and strengths. We'll look at a couple of the big names that people often turn to.
UltraVNC: A Community Favorite
UltraVNC is a name you'll hear a lot when people talk about free VNC solutions. It's been around for a while and has a strong community behind it, which means there's a lot of support if you run into questions. It's a very versatile tool, and many users, like myself, have found it quite reliable for connecting to various machines. I've even had it running on a couple of PCs that I was already logged into using RDP, which, you know, shows its flexibility. It's a pretty robust choice for a free program, and many people swear by it.
Getting Started with UltraVNC
Setting up UltraVNC can be quite straightforward, but sometimes you need a very specific kind of installation. For instance, some folks just need the VNC server part installed, registered as a service so it starts automatically with Windows, and then they need to set a password for access. I've seen other posts where people share scripts for this, and it's a rather clever way to automate the process. A batch script, for example, could be made to run on computer startup to silently install UltraVNC when the operating system restarts. This is incredibly useful for deploying it across multiple machines without a lot of manual work, and it's something many IT pros appreciate, too.
When you're getting it going, you'll definitely want to make sure that port 5900 is open on your network. That's the standard port VNC uses, so it's, like, super important for allowing your computer to be reached via VNC once everything is installed. Setting your password during the script installation is also a critical step, obviously, because you want to keep your remote connections secure. It's all about getting those initial pieces in place so that the system can do its job without much fuss, you know.
Tackling Common UltraVNC Hurdles
While UltraVNC is great, you might run into a few little bumps. For example, some users have noticed that if the `ddengine` (which is a display driver component) is turned off, the connection works fine, but when they try to switch to a second screen, two screens appear, but you just can't actually go to the second one. This can be a bit frustrating if you're working with multi-monitor setups. It's one of those things that can crop up, and it's good to be aware of it, like, just in case it happens to you.
Another thing that can be a bit tricky is file transfer. I know of a customer with an older Siemens industrial PC running UltraVNC 1.0.5 release (which, apparently, was an original Siemens installation, and they weren't allowed to upgrade anything), and file transfer simply didn't work for them. This shows that older versions or specific industrial setups might have limitations. Also, sometimes the mouse pointer can look like just a dot instead of a regular arrow. If that happens, you can put `Localcursor=2` into your *.vnc link line, and you'll see a normal mouse pointer again, which is, you know, a pretty neat trick to know.
If you ever have issues, checking the logs can be a real lifesaver. You could activate logging in the VNC server settings and then take a look at the resulting log file. Checking the debug info to the `winvnc.log` file in UltraVNC admin properties can give you a lot of clues about what's going on, which is, like, really helpful for troubleshooting, honestly. It's all about gathering information when things don't quite go as planned.
TightVNC: Speedy and Streamlined
TightVNC is another excellent free option for Windows users, and it's definitely worth considering. It's a remote control package that, like UltraVNC, comes from the original VNC project, but it has quite a few new features, improvements, and bug fixes over that standard version. People often talk about it as a very lightweight, fast, and reliable piece of remote control software, which is, you know, exactly what you want when you're trying to manage something from a distance. It's really good at what it does, and it's been around for a good while, too.
Why TightVNC Stands Out
One of the really cool things about TightVNC is how well it works with slow network links. If you're trying to connect over, say, a modem or a less-than-perfect internet connection, TightVNC tends to perform quite admirably. It's designed to be efficient with bandwidth, which means you get a smoother experience even when your connection isn't the fastest. This makes it a great choice for those remote IoT devices that might be in locations with spotty internet, or for people who are just, you know, dealing with older network setups. Its current version, 1.2.0, has seen a lot of changes and improvements, making it a pretty solid option for most folks.
Setting Up TightVNC
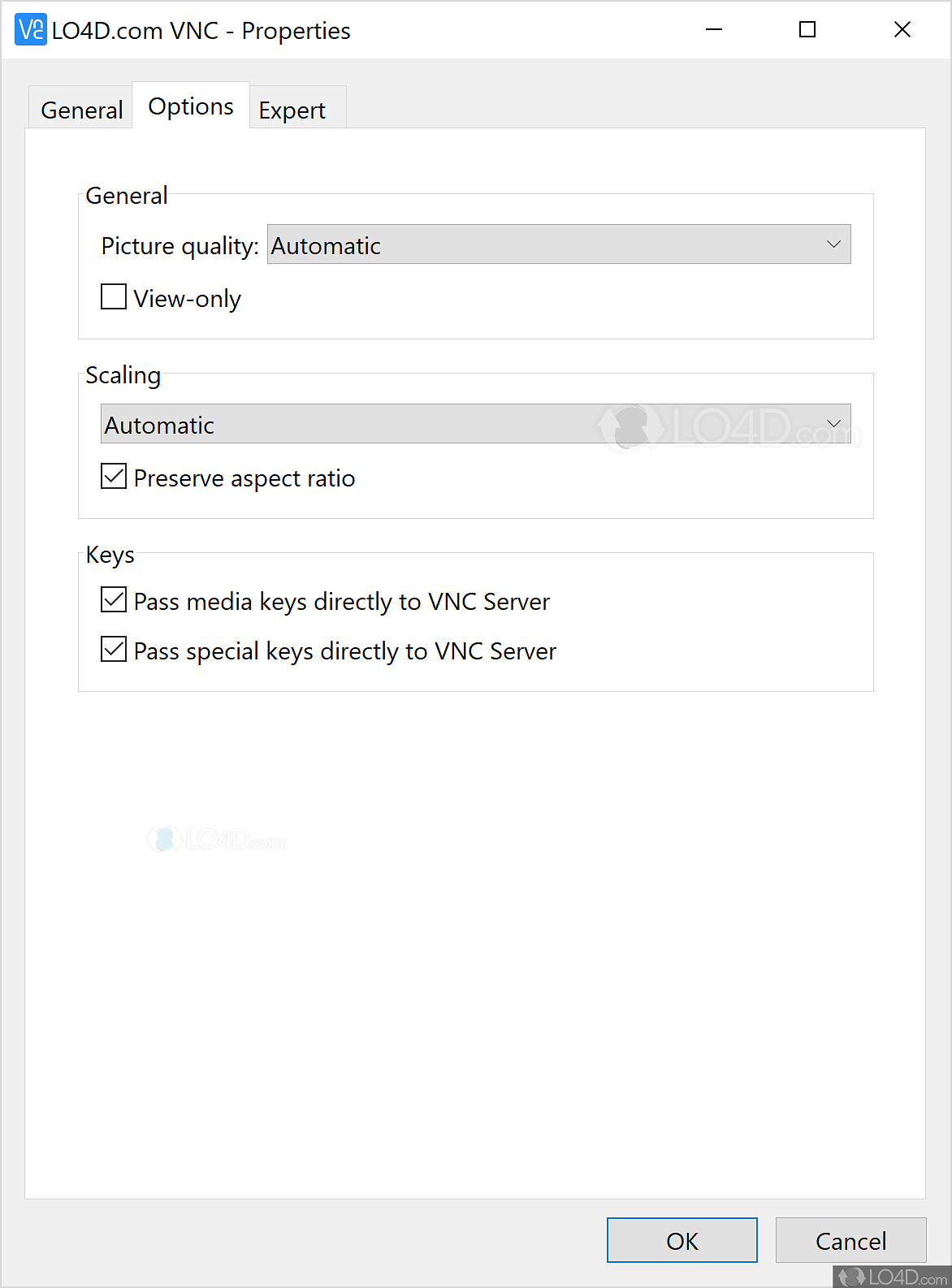
Getting TightVNC up and running is pretty similar to other VNC solutions. You'll need to download and install the TightVNC server on the remote PC you want to control. For Windows machines, many people consider TightVNC server to be a top choice for remote desktop access. The process is generally straightforward, and you'll find it lets you remotely control another PC over a network, giving you access to its desktop and all its applications. It's a fairly simple setup, and you can get it from places like FileHorse, which is, like, a common spot for downloads.
RealVNC Connect and Free Alternatives
Beyond UltraVNC and TightVNC, there's also RealVNC Connect, which is sometimes called RealVNC. This operates as remote access software that really lets you control and manage computers securely across the entire world. It's known for being straightforward and easy to use, which is a big plus for many people. While RealVNC Connect has paid tiers, there are often free versions or trial options that let you get a taste of its capabilities. There's also RealVNC Free, which enables you to remotely access and control other PCs over the internet, making it easier for collaboration and troubleshooting, which is, like, really useful for teams or helping friends out. So, you have options, you know, even if you want to stick with the free stuff.
VNC Clients for On-the-Go Control
Being able to control your remote computers or IoT devices from your main PC is great, but what about when you're out and about? That's where mobile VNC clients come into play. Having an app on your phone or tablet that lets you connect to your VNC server can be incredibly convenient, especially for quick checks or adjustments. It's, like, having your remote desktop right in your pocket, which is pretty amazing, if you ask me.
Android VNC Clients: AVNC and Beyond
For Android users, there are several VNC client options available. One that often gets good reviews is AVNC. I've heard from users who say it works perfectly with UltraVNC, which is, you know, a really good sign of compatibility. It's also open source, which many people appreciate, and it renders pretty fast, meaning you get a smooth experience on your mobile device. Having a reliable Android VNC client means you can check on your industrial PC or your home server while you're grabbing a coffee, which is, like, a huge benefit for busy people. It's all about convenience and staying connected, basically.
Security and Best Practices for Your VNC Setup
Whenever you're dealing with remote access, security is, like, super important. You're essentially opening a door to your computer or device from the outside world, so you want to make sure that door is well-guarded. It's not just about getting the free download; it's also about using it wisely and safely. Nobody wants their system to be, you know, easily accessible to just anyone, so taking a few precautions is always a good idea.
Keeping Your Connection Safe
So, is VNC safe to use for remote access? Well, it can be, but you need to take steps to make it so. First off, always use strong, unique passwords for your VNC server. Don't use something simple that someone could guess easily. Secondly, consider using VNC over a secure connection, like a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts all the traffic between your client and server, adding a thick layer of security. This is, like, a really good idea, especially if you're connecting over public Wi-Fi. Also, make sure your VNC software is up-to-date, as updates often include security fixes. It's all about being proactive and protecting your digital space, you know.
VNC vs. RDP: Which One Is Right?
You might also wonder about the difference between VNC and RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol). Both let you control a computer from afar, but they work a little differently. RDP is a Microsoft-specific protocol, meaning it's mostly used for connecting to Windows machines. When you connect via RDP, the remote computer's physical display might show a locked screen, or it might create a new, separate session for you. VNC, on the other hand, is cross-platform, so you can use it to connect to Windows, Linux, macOS, and other systems. It typically shares the existing desktop session, meaning you see exactly what someone sitting at the physical machine would see. So, if you need to access a non-Windows machine, or if you want to see the actual desktop someone else is using, VNC is often the way to go. If you're just connecting to a Windows server and want your own session, RDP might be more suitable. It really depends on what you're trying to do, basically.
Setting Up a VNC Server: A Quick Guide
Getting a VNC server running on your remote computer is the first big step to gaining distant control. It might sound a bit technical, but it's actually pretty straightforward once you know the basic steps. Whether you're using UltraVNC, TightVNC, or another option, the core idea is pretty much the same. It's about getting that server program installed and configured so it's ready to accept connections, you know, from your client device.
Step-by-Step Installation
To set up a VNC server on a remote computer, you'll usually start by downloading the server software from the official website of your chosen VNC program. For example, if you're going with UltraVNC, you'd head to their site to grab the installer. Once you have the file, you run it on the remote computer. During the installation, you'll typically be asked if you want to install the server, the viewer, or both. You'll definitely want the server component for the remote machine. You'll also be prompted to set a password for incoming connections, which, as we talked about, is super important for security. After installation, you might need to configure it to run as a service, so it starts automatically with the operating system, and make sure that port 5900 is open on the firewall. It's a pretty logical sequence of steps, and most installers walk you right through it, which is, like, very helpful. You can learn more about UltraVNC here if you want to check out their official site. Learn more about VNC solutions on our site, and link to this page .
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people often have about VNC and remote access, which, you know, come up quite a bit.
Is VNC safe to use for remote access?
Yes, VNC can be safe, but it really depends on how you set it up. Using strong passwords, encrypting your connection with a VPN, and keeping your software updated are all, like, very important steps to keep things secure. Without these precautions, any remote access tool can be a bit risky, so it's all about being smart with your setup.
What is the difference between VNC and RDP?
Basically, VNC is a cross-platform tool that shares the actual desktop session of the remote computer, so you see what's physically on the screen. RDP, or Remote Desktop Protocol, is mainly for Windows and often creates a separate session for you, so the physical display might be locked. VNC is generally more flexible for different operating systems, while RDP is often preferred for Windows server administration, you know, for its specific features.
How do I set up a VNC server on a remote computer?
Setting up a VNC server involves downloading the server software (like UltraVNC or TightVNC) onto the remote machine, running the installer, and making sure to install the server component. You'll need to set a strong password for access and, like, very importantly, ensure that the standard VNC port (usually 5900) is open on the remote computer's firewall. Many installers also let you set it up as a service so it starts automatically, which is, you know, pretty convenient.
- Securely Connect Remoteiot P2p Ssh Download Free
- Tom Six Net Worth
- Suzanne Ad Wilkinson
- Sexy Videocom
- Best Raspberry Pi Remoteiot Software For Android

Detail Author:
- Name : Elton Hammes
- Username : ahmad.morar
- Email : sgleichner@jaskolski.com
- Birthdate : 2001-07-07
- Address : 261 Santa Hollow Keithport, NV 52125-2974
- Phone : (610) 524-8447
- Company : Howe, Crona and Sipes
- Job : Food Scientists and Technologist
- Bio : Consequatur labore numquam nemo adipisci. Tempore quibusdam velit ea atque corrupti ut. Et nesciunt fugit in assumenda nobis aut.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/sanford_dev
- username : sanford_dev
- bio : Quo nihil corrupti dolorum reiciendis reiciendis.
- followers : 4363
- following : 1049
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/sschaden
- username : sschaden
- bio : Ad possimus non et voluptatum assumenda est consequatur.
- followers : 6815
- following : 2495
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/sanford_schaden
- username : sanford_schaden
- bio : Necessitatibus ipsum architecto animi omnis. Sed incidunt harum corporis autem et. Tempore magni id doloremque quae consectetur sed.
- followers : 3923
- following : 1525
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/schadens
- username : schadens
- bio : Iusto in vitae corrupti. Ullam ut dolores rerum quibusdam dicta excepturi explicabo.
- followers : 2375
- following : 1439
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@sschaden
- username : sschaden
- bio : Assumenda esse et quia et sit suscipit nemo.
- followers : 4777
- following : 2638