Keeping an eye on your internet-connected devices from afar, that's what remote IoT monitoring is all about, you know? It’s pretty important for everything from smart homes to industrial setups. Imagine having sensors spread across a big area, perhaps monitoring environmental conditions or machinery. How do you check in on them, gather information on reported data, or even fix something without being right there? This is where secure shell, or SSH, comes into the picture, offering a really solid way to connect with these devices, almost like having them right in front of you.
For anyone working with these smart gadgets, getting a good grasp on remote access is, you know, absolutely key. It’s not just about seeing numbers; it’s about making sure everything is running smoothly, keeping things safe, and getting those important updates out. Just like you'd download the YouTube app for a richer viewing experience on your smartphone, downloading the right SSH tools can truly give you a much better way to interact with your remote devices, making your life a whole lot easier, actually.
This article will walk you through the ins and outs of using SSH for your remote IoT monitoring needs. We’ll talk about why it’s such a good choice, how to get it set up, and some smart ways to keep everything secure. By the end, you’ll have a much clearer idea of how to manage your devices from anywhere, ensuring they’re always working their best, and you’re always in control, sort of.
- Norman Lear Net Worth
- Joe Wen Net Worth
- Kristin Nelson
- Cristina Carmella Onlyfans
- Garrett Phillips Update 2025
Table of Contents
- What is Remote IoT Monitoring, Really?
- Why SSH for IoT Devices, You Might Ask?
- Getting Started: How to Download and Use SSH for Remote IoT Monitoring
- Good Habits for Secure Remote IoT Access
- Typical Hurdles and How to Jump Them
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Making Your IoT Monitoring Smarter
What is Remote IoT Monitoring, Really?
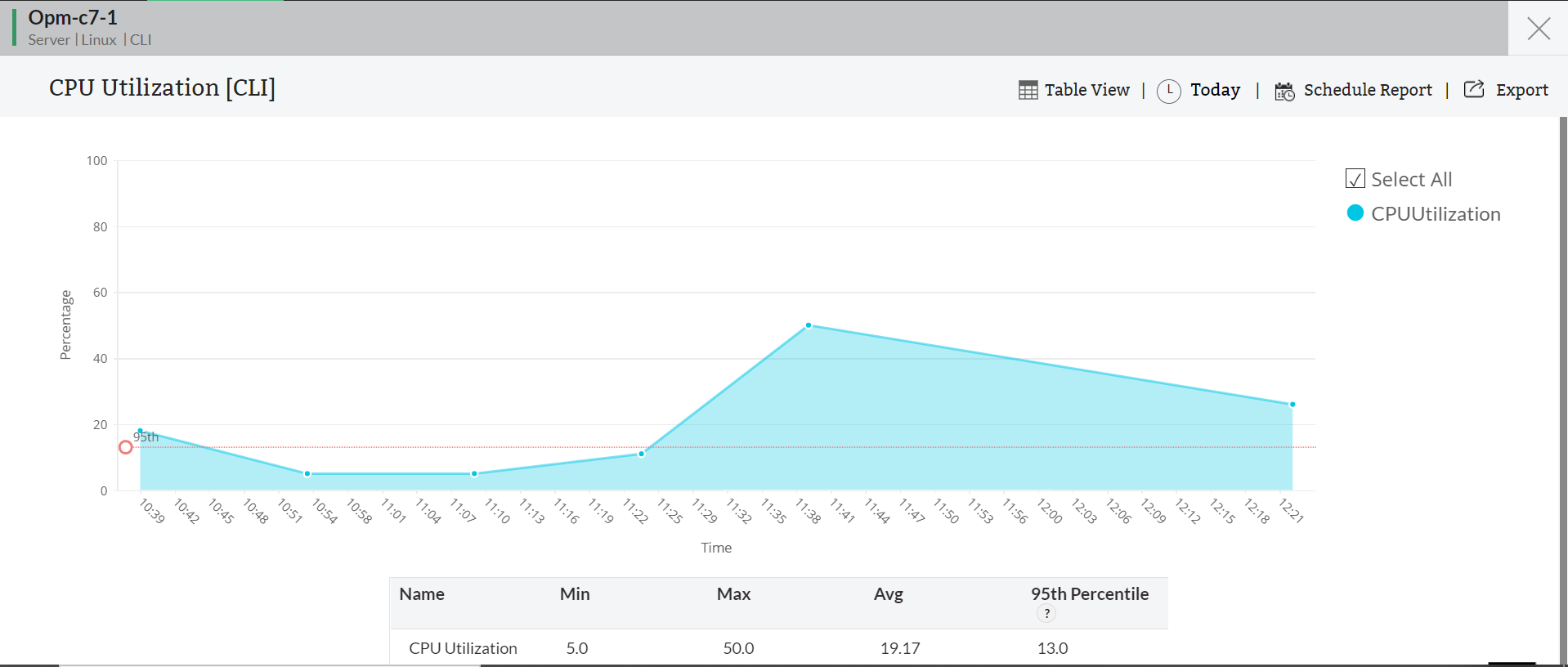
Remote IoT monitoring is about keeping tabs on your smart devices, sensors, and gadgets when you're not physically near them. It means collecting data, checking their status, and sometimes even sending commands to them from a different spot. This can be super useful for many things, like watching the temperature in a remote greenhouse or checking the performance of machinery in a factory that’s, you know, far away. It helps you make quick decisions and keeps things running smoothly, actually.
Think of it this way: just like signing in to YouTube allows you to access features like subscriptions, playlists, and purchases, and history, remote monitoring gives you access to your device's operational history and current data streams. It's about getting the full picture, even when you're miles away. This way, you can react to problems fast or make adjustments without having to travel, which is pretty convenient, really.
This whole idea becomes even more important as we put more and more smart devices into the world. Being able to connect with them safely and reliably is, well, just something you need to do. It ensures that your smart systems are always working for you, not against you, and you can always get information on reported issues, so to speak.
- Phoenix Zip Code Map
- Who Would Win In A Fight Generator
- Best Remoteiot Platform Raspberry Pi
- Twinkle Khanna Zodiac Sign
- Nicole Carter Cause Of Death
Why SSH for IoT Devices, You Might Ask?
SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is a network protocol that lets you connect to a computer or device over an unsecured network, but in a very secure way. For IoT devices, this is a really big deal. Many IoT gadgets are small, maybe not super powerful, and they often sit in places where physical access is a bit of a pain. SSH gives you a secure way to talk to them, which is very important, you know.
It’s like having a secret, protected line directly to your device. You can send commands, grab files, or even set up tunnels for other services, all without worrying too much about someone listening in. This level of security and control is, arguably, unmatched by many other simple remote access methods. It’s pretty much the gold standard for remote administration, especially for devices that are often, you know, out in the open or in less protected environments.
Using SSH means you can manage a variety of products in your IoT setup, from tiny sensors to more complex gateways, all with a consistent and secure method. It simplifies things quite a bit, actually, allowing you to focus on the data and the device's purpose rather than the security of your connection, more or less.
Solid Security Advantages
The main reason people choose SSH is for its strong security. It encrypts all the communication between your computer and the IoT device. This means that if someone tries to snoop on your connection, all they’ll see is scrambled data, which is pretty useless to them. This protection applies to your login details, the commands you send, and any data you transfer, you know.
SSH also uses something called public-key cryptography, which is a very robust way to verify who you are. Instead of just a password, you can use a pair of keys: a public one on the device and a private one on your computer. This makes it much harder for unauthorized people to get in, even if they guess your password. It’s a bit like having a very special lock that only your unique key can open, rather than a simple combination, so.
This secure setup is especially important for IoT devices that might be, you know, sitting in public spaces or connected to less secure networks. It helps keep your data safe and prevents bad actors from taking control of your devices, which is, actually, a huge relief.
Direct Command-Line Control
With SSH, you get direct access to the device’s command line. This is a powerful way to interact with your IoT gadget. You can run programs, change settings, check system logs, and diagnose problems, all by typing commands. It’s a very efficient way to manage things, especially for devices that don't have a fancy graphical interface, or even a screen, actually.
This direct control means you can perform deep maintenance tasks, troubleshoot issues in real-time, or even restart services if something goes wrong. It’s like being able to open the hood of a car and adjust things directly, rather than just pressing buttons on the dashboard. This gives you more time to tell your stories, showcase what your devices are doing, and truly understand their operational health.
For developers and system administrators, this level of control is, you know, absolutely essential. It allows for precise management and quick fixes, which is very important when you're dealing with a distributed network of devices, more or less.
Handy File Transfer Capabilities
SSH isn't just for sending commands; it’s also great for moving files around. You can use tools like SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) or SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) to securely upload new software updates, download data logs, or grab configuration files from your IoT devices. This is incredibly useful for maintenance and data collection, actually.
Imagine needing to push a new firmware update to a hundred devices at once. With SSH, you can script this process, making it very efficient and secure. Or, if a device is collecting environmental data, you can regularly download those data files for analysis. It’s a bit like having a very secure postal service directly to each of your devices, delivering exactly what you need, when you need it, you know.
This capability makes SSH a comprehensive solution for remote IoT management. It covers both command and data transfer, providing a full suite of tools for keeping your devices in top shape, which is, arguably, a big plus.
Getting Started: How to Download and Use SSH for Remote IoT Monitoring
Getting set up with SSH for your IoT devices isn't too complicated, but it does involve a few steps. The good news is that once you have it going, managing your devices becomes a lot easier. The first thing you'll need is an SSH client on your computer, and then you'll configure your IoT device to accept SSH connections, which is pretty straightforward, actually.
It’s very much like getting ready for a trip: you need the right vehicle (your SSH client) and your destination needs to be ready to receive you (your IoT device configured for SSH). This preparation ensures a smooth and secure connection, letting you access features like device logs and settings without a hitch. You want to make sure you’re getting the directions for your account, so to speak, for both your computer and your device.
Remember, the goal here is to establish a reliable and secure channel. Taking the time to set this up correctly will save you a lot of headaches down the road, and it will give you peace of mind knowing your devices are accessible and protected, more or less.
Picking Your SSH Client
For most operating systems, you probably already have an SSH client built-in. If you use Linux or macOS, you can just open your terminal application and type `ssh`. It’s usually there, ready to go. For Windows users, things have gotten much easier. Modern versions of Windows 10 and 11 actually include an OpenSSH client by default, so you can use PowerShell or Command Prompt, which is pretty handy, you know.
If you're on an older Windows system or prefer a graphical interface, a very popular choice is PuTTY. It’s a free and open-source client that’s been around for ages and works really well. You can download it from its official website, and it’s a fairly small program that’s easy to install. Just search for "PuTTY download" and you'll find it, you know, pretty quickly.
When picking your client, think about what you’re comfortable with. Command-line tools offer a lot of flexibility, while graphical ones can be a bit more user-friendly for beginners. Either way, having a reliable client is the first big step in your remote IoT monitoring journey, actually.
Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
Most popular IoT platforms and single-board computers, like Raspberry Pi, come with SSH capabilities that you can easily enable. For a Raspberry Pi, for instance, you can enable SSH through its configuration tool (raspi-config) or by simply placing an empty file named `ssh` (no extension) into the boot partition of the SD card before you even start it up. This is a really simple trick, actually.
For other devices, the process might be a bit different, but it usually involves checking the device's documentation for how to enable SSH. Sometimes it’s a setting in a web interface, or you might need to flash specific firmware. The key is to make sure the SSH server (often called `sshd`) is running on your IoT device, and that it’s set to start automatically when the device boots up, so.
It’s also a very good idea to change the default password for your device immediately after enabling SSH. Many devices come with common default usernames and passwords (like `pi`/`raspberry` for a Raspberry Pi), which are, arguably, a huge security risk. Think of it like getting a new car; you wouldn't leave the keys in the ignition, would you? This step is absolutely crucial for keeping your devices safe, more or less.
Making Your First Connection
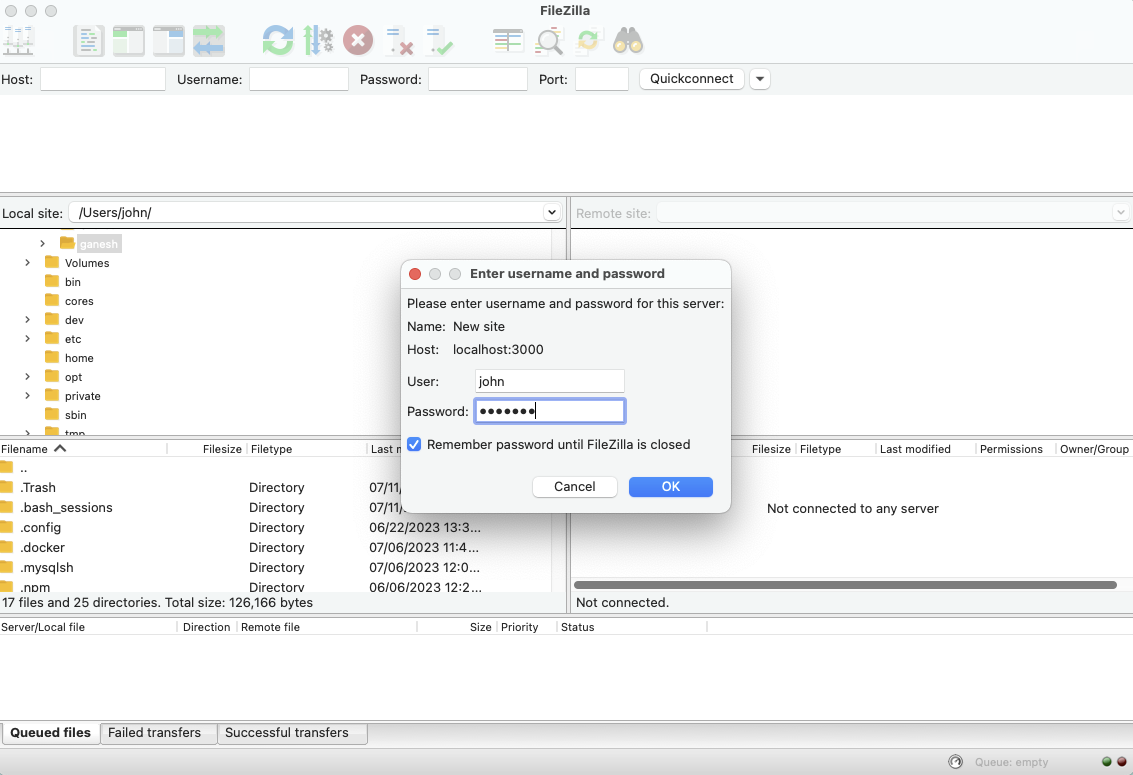
Once your SSH client is ready and your IoT device has SSH enabled, you can make your first connection. You'll need the IP address or hostname of your IoT device and the username you want to use. The basic command in a terminal looks like this: `ssh username@device_ip_address`. So, for a Raspberry Pi, it might be `ssh pi@192.168.1.100`, you know.
The first time you connect, your client will probably ask you to confirm the device’s "fingerprint." This is a security measure to make sure you’re connecting to the right device and not some imposter. Just type `yes` if it matches what you expect (or if you’re connecting for the first time, it's usually safe to accept). Then, you'll be prompted for your password, which is, you know, the one you hopefully changed from the default.
After successfully entering your password, you’ll see a command prompt for your IoT device. Congratulations! You're now securely connected and can start sending commands, checking data, or transferring files. It’s a pretty good feeling to have that kind of remote control, actually, almost like you’re right there with the device.
Good Habits for Secure Remote IoT Access
Having SSH enabled is a great start, but keeping your remote IoT setup truly secure requires some ongoing good habits. Just like you'd maintain your car at an auto center for repair & maintenance, your digital devices also need regular care. Security isn't a one-time thing; it's a continuous process, especially when you're dealing with devices that are, you know, often exposed to the internet.
Thinking about security from the very beginning can save you a lot of trouble later on. It’s about building a strong foundation for your remote monitoring system, ensuring that your data stays private and your devices remain under your control. These practices help protect against potential threats and keep your operations running smoothly, which is, arguably, very important.
By following these tips, you can make your remote IoT monitoring system much more resilient against attacks and ensure that your access remains exclusive to authorized users, which is, you know, the whole point of using SSH in the first place.
Stronger Authentication Methods
While passwords work, using SSH keys for authentication is a much stronger and more secure approach. SSH keys are much longer and more complex than typical passwords, making them nearly impossible to guess. You generate a pair of keys: a public key that goes on your IoT device and a private key that stays securely on your computer. When you connect, the two keys "talk" to each other to verify your identity, so.
It’s a bit like having a very unique digital handshake that only you and your device know. This method eliminates the risk of brute-force attacks where someone tries to guess your password over and over again. Plus, you can even disable password-based login on your IoT devices entirely once you have key-based authentication set up, which is, actually, a fantastic security boost.
Always protect your private key with a strong passphrase, even if it's on your computer. This adds another layer of security, meaning that even if someone gets hold of your private key, they still can't use it without the passphrase. It's a very simple step that makes a huge difference, you know.
Keeping Things Up-to-Date
Software, including the operating system and any applications on your IoT devices, should be updated regularly. Updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities that bad actors could exploit. Running outdated software is, arguably, like leaving a door unlocked for potential intruders. It's a common oversight that can lead to big problems, actually.
Set up a schedule for checking and applying updates to your IoT devices. This might involve remotely connecting via SSH and running update commands (like `sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade` on Debian-based systems). It’s a bit like getting your car’s oil changed; it’s routine maintenance that keeps everything running well and prevents bigger issues down the road, you know.
Keeping your SSH client on your computer updated is also important. Newer versions often have improved security features and bug fixes. Staying current across the board is a very simple yet effective way to maintain a strong security posture for your remote IoT monitoring, more or less.
Smart Network Separation
If possible, put your IoT devices on a separate network segment or VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) from your main home or business network. This is called network segmentation. If an IoT device were to be compromised, this separation would help prevent the attacker from easily moving to other, more sensitive parts of your network, which is, you know, a very smart defense.
Think of it like having different rooms in a house with separate locks. If one room is broken into, the rest of the house is still secure. You can configure your router or network switches to create these separate segments. This might sound a bit technical, but many modern routers offer fairly straightforward ways to do this, actually.
Also, limit the ports that are open on your IoT devices to only those absolutely necessary. For SSH, this usually means just port 22. Closing other unnecessary ports reduces the "attack surface" – the number of ways someone could try to get in. It's a very basic firewall principle that adds a lot of security, you know.
Typical Hurdles and How to Jump Them
Even with the best intentions, you might run into a few snags when setting up or using remote IoT monitoring with SSH. One common issue is devices changing their IP addresses, especially if they’re using DHCP. If your device's IP changes, your SSH command might suddenly stop working, which is, you know, pretty frustrating.
A good solution for this is to assign a static IP address to your IoT device within your local network, or use a hostname if your network supports it. Another option is to use a dynamic DNS service if you need to access devices from outside your local network and don't have a static public IP. This way, you always connect to a name (like `myiotdevice.dyndns.org`) rather than a changing number, so.
Another challenge can be dealing with firewalls, both on your local network and on the internet service provider's side. If you can't connect, check if port 22 (the default for SSH) is blocked. You might need to configure port forwarding on your router to allow outside connections to reach your IoT device. Just remember to do this carefully and only open ports you absolutely need, you know, for security reasons.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people often have about using SSH for remote IoT monitoring:
What if my IoT device doesn't have enough memory for an SSH server?
Many small IoT devices, even those with limited resources, can run a lightweight SSH server. OpenSSH is quite efficient, and there are even smaller alternatives if needed. Check your device's specifications and the documentation for its operating system. Usually, if it can run an operating system like Linux, it can probably handle SSH, actually.
Is it safe to expose my IoT device's SSH port to the internet?
Exposing any port directly to the internet carries some risk. If you must do this, it’s absolutely critical to use SSH key-based authentication, disable password logins, change the default SSH port from 22 to a non-standard one, and keep your software updated. For even greater security, consider using a VPN to create a secure tunnel to your network, then connect to your IoT devices within that tunnel, you know.
Can I use SSH to monitor sensor data in real-time?
While SSH is great for command-line access and file transfers, it's not typically used for real-time streaming of sensor data. For that, you might use protocols like MQTT or HTTP, which are designed for efficient data transmission. However, you can use SSH to set up or troubleshoot those data streaming services, or to retrieve logs that contain historical sensor data, so it still plays a very important role, actually.
Making Your IoT Monitoring Smarter
Getting your head around remote IoT monitoring with SSH is a pretty big step towards having truly smart and secure connected systems. It gives you the power to reach out to your devices, check their pulse, and make adjustments no matter where you are. Just like you'd visit a Penticton, BC store for automotive, tools, household, sports, toys & outdoor products, or stop by at the auto center for repair & maintenance, you need the right tools and approach for your digital gadgets.
By using SSH, you’re not just connecting; you’re building a secure bridge that protects your data and keeps your devices under your command. This means you can keep things running smoothly, get information on reported issues, and make sure your smart spaces are always working just the way you want them to. It’s about having that control, that peace of mind, which is, you know, pretty valuable in today's world.
So, take these steps, try out these methods, and start making your remote IoT monitoring truly effective and secure. Learn more about secure device access
- Belle Delphine Leaked
- Queenpussybossv Only Fans Leak
- Obsession In Synastry
- Rac Musician Net Worth
- Gawain Rushane Wilson
Detail Author:
- Name : Prof. Caitlyn Lindgren IV
- Username : dietrich.brown
- Email : rylan.runte@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1998-05-07
- Address : 8574 Ruthie Islands Noemyburgh, GA 31502
- Phone : 743-286-9233
- Company : Lehner, Little and Skiles
- Job : Tree Trimmer
- Bio : Qui aut blanditiis a qui unde consectetur excepturi. A tempora delectus eum qui. Cumque vitae in illum ex quisquam adipisci doloremque.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@mariane_hudson
- username : mariane_hudson
- bio : Dolor ut commodi minima. Aspernatur et vel laborum libero fugit.
- followers : 2455
- following : 87
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/hudsonm
- username : hudsonm
- bio : Inventore assumenda perferendis ab sit non est in.
- followers : 2120
- following : 2075
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/mhudson
- username : mhudson
- bio : Porro perferendis quis dicta minima et atque et.
- followers : 5639
- following : 2556
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/mariane_official
- username : mariane_official
- bio : Deserunt omnis consectetur veniam ab quos sint. Debitis repellat molestiae qui delectus qui temporibus totam. Et nulla nostrum quae recusandae assumenda qui.
- followers : 1347
- following : 829
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/mhudson
- username : mhudson
- bio : Quae aut in et explicabo quis. Sit iusto id magnam optio sequi quis.
- followers : 3692
- following : 2457